The Great Safe Debate: Where Should You Stash Your Valuables?
Imagine waking up to a break-in—your emergency fund gone in minutes. Or arriving at your bank only to find their vault sealed for “maintenance” when you urgently need access. These aren’t just nightmares; they’re real risks when choosing how to protect your assets.
Financial security hinges on one critical decision: institutional storage or private safeguarding. Bank-held compartments promise robust defenses but operate on restrictive schedules. Personal vaults offer immediate control yet demand meticulous setup. Between these two options, which truly delivers peace of mind when safeguarding what matters most?
This clash isn’t about mere metal boxes—it’s a battle between trust in systems and self-reliance. We’ll expose overlooked vulnerabilities, compare hidden expenses, and reveal which option stands firm against disasters, thieves, and unforeseen crises. Your money’s safety deserves more than guesswork. Let’s settle the debate.
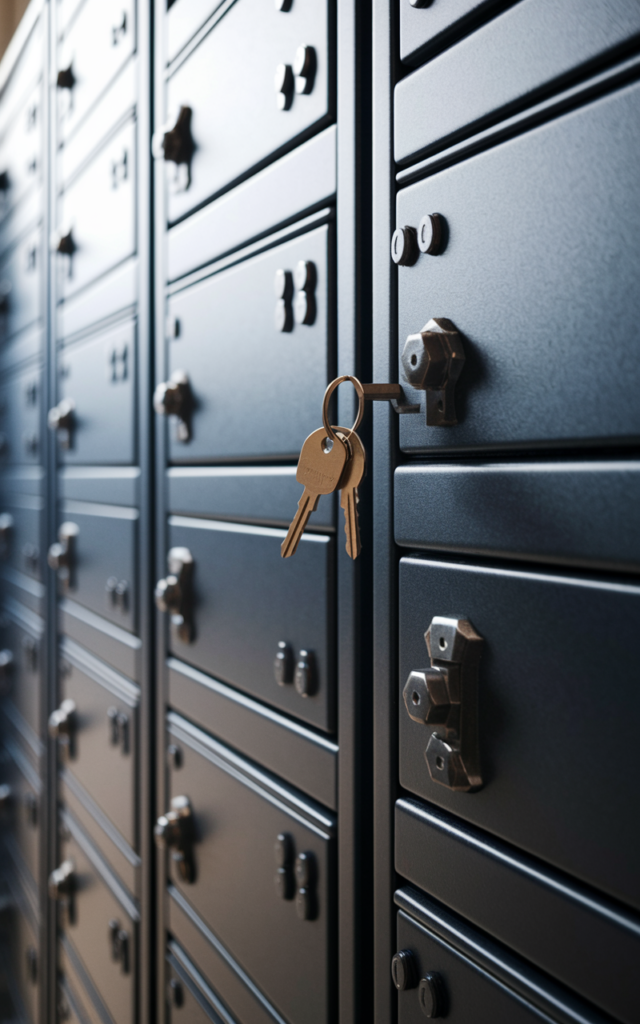
What Is a Bank Vault Storage Unit?
These secure compartments, typically housed within financial institutions or specialized security facilities, offer clients a shielded space to store precious items. Think of them as ultra-secure rental spaces where only you hold the key—literally.
How These Secure Units Operate:
- Dual-key system (your physical key + the institution’s master key)
- Limited access during business hours only
- No insurance coverage from the hosting facility

Where You’ll Find These Services:
• Traditional banking institutions (most common)
• Private high-security storage facilities
• Some credit unions and trust companies
The system works simply: You rent the space, store your valuables, and return when needed. But this convenience comes with strings attached—restricted access times, potential government seizures during investigations, and surprising limitations on what you’re allowed to store.
Unlike keeping possessions at your residence, these solutions provide institutional-grade protection against theft and disasters. However, that ironclad security means sacrificing immediate availability—a trade-off that doesn’t work for everyone’s needs.
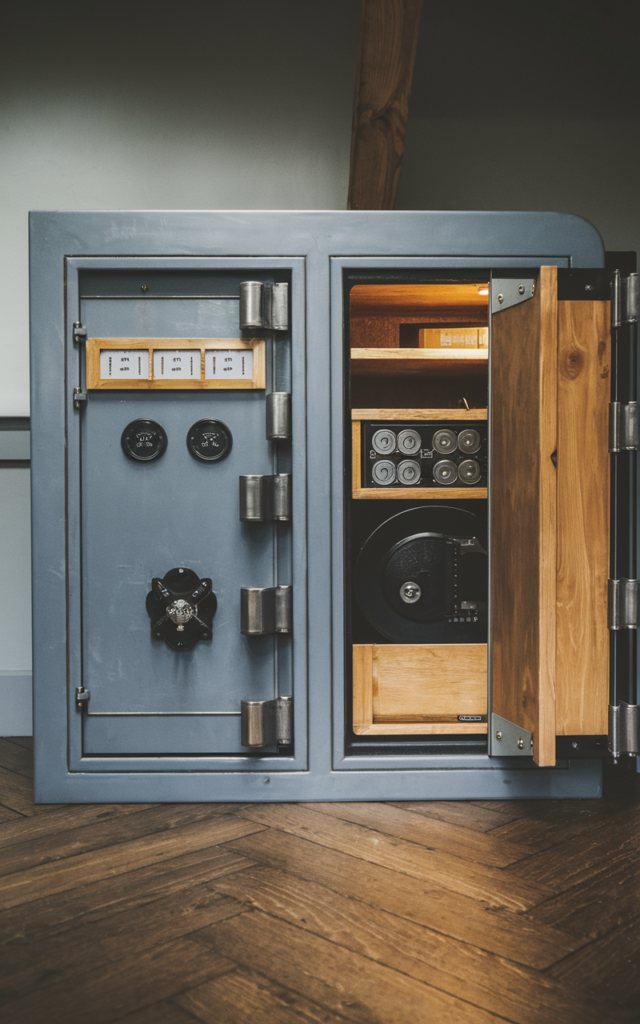
Your Personal Fortress: Understanding Residential Security Solutions
A residential security vault serves as your private stronghold for protecting valuables without relying on external facilities. These self-contained units come in various configurations to match different protection needs and living spaces.
Primary Varieties of Domestic Protection Units:
- Wall-Embedded Models – Discreetly built into your home’s structure
- Floor-Anchored Designs – Heavy-duty options bolted to your foundation
- Portable Security Cases – Compact, movable versions with basic protection
Beyond Currency Storage – Versatile Applications:
• Critical document preservation (titles, passports, contracts)
• Jewelry and family heirlooms safeguarding
• Medication storage for controlled substances
• Firearm security in gun-friendly households
• Digital media backup protection (external drives, USBs)
Protection Showdown: Institutional vs. Residential Asset Security
When safeguarding your financial reserves, the battle between professional vaults and personal storage solutions presents critical differences in defense capabilities. Let’s examine how these options measure up against modern threats.
Fortress-Level Defenses Compared:
- Financial Institution Advantages:
• 24/7 monitored alarm systems
• Reinforced concrete structures
• Armed personnel and surveillance
• Mandatory access logs - Residential Unit Strengths:
• Instant availability during crises
• Customizable alert systems
• Hidden installation options
• No third-party access records
Evaluating Threat Scenarios:
- Unauthorized Access Risks
Professional facilities deter organized theft rings with multiple security layers, while residential options rely on stealth and homeowner vigilance. Most burglars target visible, unsecured items rather than challenging properly installed units. - Fire Resilience
Bank vaults typically withstand extreme temperatures longer than consumer-grade models. However, high-end residential units now offer 90+ minute fire ratings – sufficient for most house fires. - Environmental Threats
Flooding affects both options differently:
- Underground bank storage may flood during disasters
- Home installations can be elevated or waterproofed

- Human Factor Vulnerabilities
Financial institutions face internal theft risks from employees, while residential protection depends entirely on your discretion and installation quality.
Availability Showdown: Your Money When You Need It
The true test of any storage system comes when urgent situations demand immediate access to your funds. Let’s compare how these options perform when timing matters most.
Access Timelines Compared:
- Residential Units:
• Instant retrieval at any hour
• No permission requirements
• Always operational during crises - Financial Institution Storage:
• Limited to business hours (typically 9-5 weekdays)
• Possible holiday closures
• Potential processing delays
Critical Situations Where Availability Matters:
- After-Hours Emergencies
Medical bills or unexpected expenses don’t wait for banking hours. With home storage, midnight emergencies don’t become financial crises. - Power Interruptions
Modern residential units with mechanical locks remain functional during outages, while some bank systems may deny access without electricity. - Civil Unrest/Lockdowns
Recent events proved institutional access can vanish overnight during civil emergencies, while home-stored assets remain under your control. - Natural Disasters
When evacuation orders strike, bank closures often follow. Home storage allows grabbing essentials en route to safety. - Sudden Travel Needs
Last-minute trips become simpler when you’re not bound by vault access schedules.
Protection Gaps: Understanding Coverage Limitations
Many assume their valuables enjoy automatic protection, but reality reveals startling coverage gaps in both systems.
Financial Institution Liability
- FDIC insurance never extends to contents
- Most contracts explicitly deny responsibility
- Typical maximum bank liability: 500−500−10,000
- Requires proven negligence claims
- Contents valuation challenges
Residential Coverage Considerations
- Standard Homeowner Policies:
- Usually cap “cash” coverage at 200−200−500
- Require special riders for full protection
- May mandate UL-certified containers
- Policy Requirements:
- Bolting/location specifications
- Fireproofing certifications
- Theft-deterrent features
- Enhanced Protection Options:
- Scheduled personal property endorsements
- Valuable articles floaters
- Increased special limits

Critical Safeguarding Steps
For institutional storage:
- Maintain detailed inventory with photos
- Consider third-party insurance
- Verify institution’s insurance certificates
For residential protection:
- Document all contents thoroughly
- Install insurer-approved models
- Regularly update policy limits
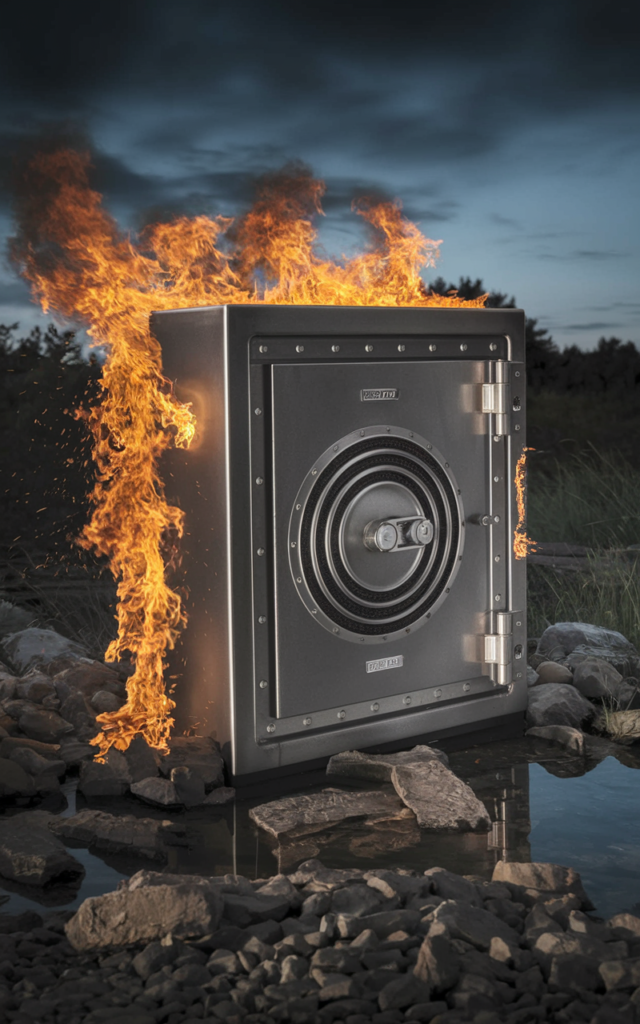
Fire & Water Resistance: Which Protects Better?
When catastrophe strikes, your storage choice determines whether valuables emerge unscathed or become casualties.
Institutional Vault Performance
- Typically rated for 2,000°F for 4+ hours
- Multi-hour flood resistance in most facilities
- Earthquake-reinforced structures in risk zones
- Professional disaster recovery protocols
Residential Unit Ratings
- Fire Endurance Standards:
• UL Class 350: 1-2 hour protection (1700°F)
• ETL Verified alternatives
• Paper survival vs. media protection differences - Water Intrusion Protection:
• IP ratings for moisture resistance
• True waterproof vs. water-resistant claims
• Gasket quality and seal longevity - Combined Threat Models:
• Simultaneous fire/water testing
• Post-disaster functionality guarantees
• Warranty exclusions review
Real-World Survival Factors
Bank vaults benefit from:
- Centralized sprinkler systems
- Professional maintenance
- Structural redundancies
Home units excel when:
- Properly installed away from risk zones
- Regularly maintained
- Paired with smoke/water detectors
The verdict? Institutional storage generally offers superior elemental protection, but premium residential units now rival bank-level safeguards at higher price points. For irreplaceable items, consider that most home fires are contained within 30 minutes – making UL-rated 1-hour protection often sufficient for residential scenarios. Always verify independent testing documentation rather than relying on manufacturer claims alone.
Size & Storage Capacity: What Fits Your Needs
Your protection solution must accommodate both current possessions and future acquisitions without compromising security.
Institutional Container Constraints
- Standard sizes (3″x5″ to 10″x15″ typical)
- Height restrictions (often under 24″)
- Prohibited items (liquids, weapons, hazardous materials)
- No expansion possibilities
- Shared vault space limitations
Residential Unit Versatility
- Size Spectrum:
• Compact models (0.5-2 cubic feet)
• Walk-in vault options (100+ cubic feet)
• Modular systems for growing collections - Specialized Configurations:
• Document organizers and file rails
• Adjustable shelving systems
• Weapon racks with quick-access
• Jewelry trays with anti-tarnish lining - Custom Integration:
• Closet conversion kits
• Furniture concealment options
• Floor-to-ceiling installations

Capacity Planning Insights
Financial institution storage works best for:
- Flat documents (deeds, certificates)
- Small valuables (coins, rings)
- Items rarely accessed
Residential solutions excel for:
- Bulkier items (firearms, electronics)
- Collections requiring organization
- Frequently used possessions
The space advantage clearly favors home installations, particularly for those safeguarding diverse item types or larger objects. However, those with minimal storage needs may find institutional rentals more space-efficient. Always measure your largest item before selecting any protective solution, and consider future acquisitions in your decision.
Real-Life Scenarios: When Each Option Shines
Different situations call for different security approaches. Here’s where each storage method proves most valuable.
Residential Units Excel When:
- Emergency Funds Are Needed:
- Medical crises requiring immediate cash
- Natural disaster preparations
- Sudden travel opportunities
- Business Operations Demand Access:
- Retailers needing daily change funds
- Landlords storing rental agreements
- Small businesses with nightly deposits
- Personal Items Require Regular Use:
- Frequently worn jewelry
- Active firearm collections
- Important medical documents
Institutional Storage Proves Best For:
- Priceless Heirlooms:
- Family historical documents
- Antique jewelry collections
- Irreplaceable memorabilia
- Long-Term Legal Protections:
- Estate planning documents
- Property deeds and titles
- Business contracts
- High-Value Specialty Items:
- Rare coin collections
- Collectible valuables
- Backup digital media
Hybrid Approach Wins In These Cases:
- Keeping copies of critical documents in both locations
- Storing originals professionally with home copies
- Splitting cash reserves between both options
Professional Guidance: Selecting Your Ideal Protection System
Transform your residential security strategy with these professional recommendations for choosing optimal asset protection.
Selection Criteria for Domestic Storage Solutions
- Protection Level Priorities
- Fire resistance: Minimum 1-hour UL 350 rating
- Burglary defense: TL-15 or higher rating
- Water resistance: Verified independent testing
- Size & Configuration Essentials
- Measure largest item + 25% growth space
- Consider vertical vs. horizontal layouts
- Evaluate interior organization systems
- Installation Requirements
- Minimum 750 lbs for free-standing models
- Concrete anchor compatibility
- Wall stud positioning for built-ins
- Lock Mechanism Options
- Biometric: Convenience vs. potential failures
- Electronic: Audit trails but power dependent
- Mechanical: Reliability with slower access
Pro Installation Advice
- Position away from obvious locations
- Ensure proper weight distribution
- Integrate with existing alarm systems
- Document all access codes separately
Maintenance Must-Dos
- Annual lock mechanism checks
- Biannual interior inspections
- Immediate battery replacements
- Regular seal integrity tests




